With the increase in the need for data security and the advancement of technology, companies (public, private and non-governmental organizations) have realized the need to protect the data which they hold. Information is power, and thus protecting the information that you hold as a company is critical to your success. A DPIA, Data Protection Impact Assessment is a tested and tried process that seeks to identify the chances of data being tampered with by external parties. So, when should a DPIA be carried out in your company? In this article, we seek to answer this all-important question. For more information on DPIA and GDPR, click on the following link https://ethyca.com/data-protection-impact-assessments/.
Should a DPIA be conducted on my organization? And if so when?
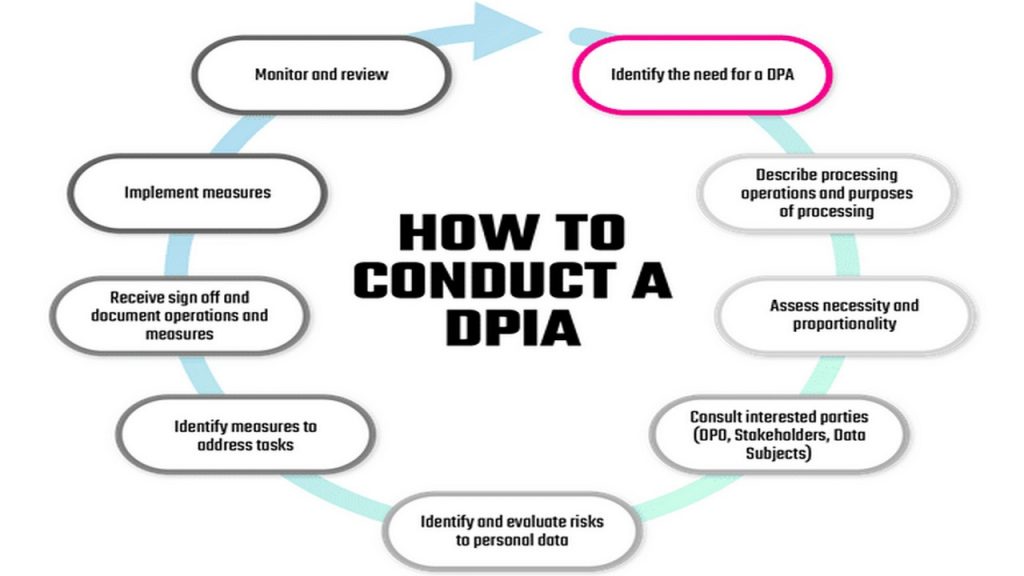
Before we answer our main subject question, we need to tackle another one. What informs a company on whether to conduct a DPIA? Europe has attempted to answer this question through the General Data Protection Regulation of 2016. The GDPR informs organizations and companies that a DPIA should be conducted when the processing of data is likely to produce a result that may infringe on the rights of other third parties.
From the language set in the GDPR, you can already surmise that the implementation of a DPIA is not mandatory but a matter of good practice. Data managers and quality assurance officers can be chief implementers of the DPIA, ensuring that the collection, processing, and storage of data are within the regulations of the GDPR.
The GDPR points out that a DPIA is to be implemented when a high-risk situation is imminent. And while it doesn’t define, it gives examples. Article 35(3) of the GDPR gives three data processing examples that automatically call for the need of a DPIA.
The three examples given are the systematic and extensive profiling with significant events, the large scale use of sensitive data, and public monitoring. What can be inferred from the examples given is that an organization that deals with data should put screening protocols that allow for it to determine the need for a DPIA.
So, when is a DPIA not required?
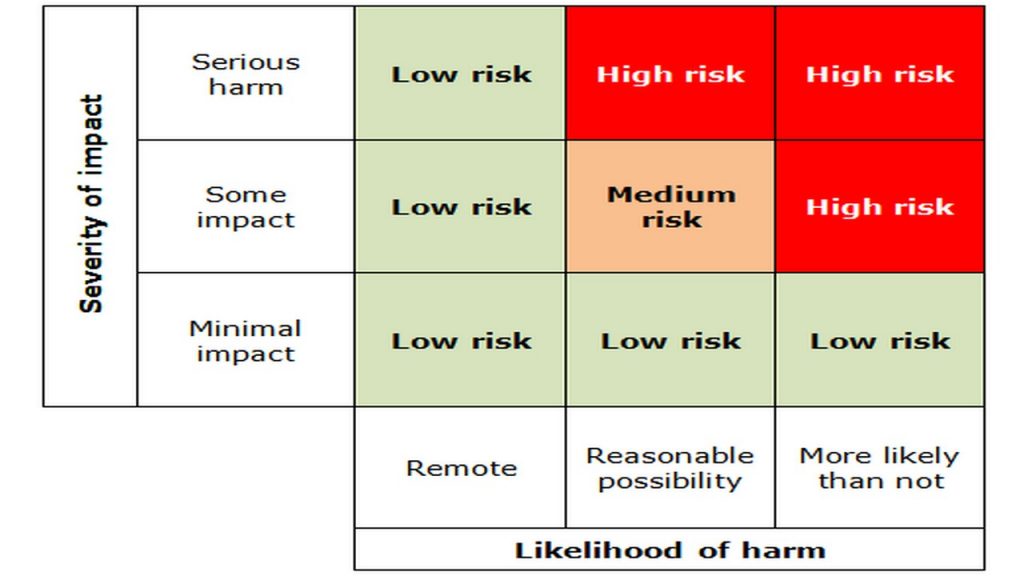
There are cases where a DPIA is not required. GDPR regulations go as far as mentioning them in Article 35(1). The first instance is implied. If there is a low risk of the rights of other parties being infringed by the processing of data in your hands, then there is no need for implementation of a DPIA.
A DPIA is also not required in the situation whereby it has been stated by law that the processing of specific data will not require a DPIA. This, of course, works with the assumption that the entity you are working for can supported by the GDPR regulations.